MULTIVIBRATOR & THEIR CLASSIFICATIONS
MULTIVIBRATOR
A multivibrator is basically a two-stage R-C coupled amplifier with positive feedback from the output of one amplifier to the input of the other. Multivibrator is a switching circuit and may be defined as an electronic circuit that generates nonsinusoidal waves such as rectangular waves, sawtooth waves, square waves, etc. Multivibrators are capable of storing binary numbers, counting pulses, synchronizing arithmetic operations and performing other essential functions used in digital systems.
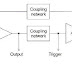
The circuit operates in two states viz. on and off controlled by circuit condition. The operation of the circuit is such that when one amplifier is cut off (off) the positive feedback loop maintains the other amplifier in a conducting or on the state. When a trigger causes one amplifier to change state, the coupling network acts to change the state of the second amplifier. The outputs are opposite in sense, one indicating a transition from an "off" state to an "on" state and the other the opposite transition. The condition in which the multivibrator may remain indefinitely until the circuit is triggered by some external signal is termed as a stable state.
There are only two possible states of a multivibrator and are as follows :
First state: Transistor Q¹ on and transistor Q² off.
Second state: Transistor Q¹ off and Transistor Q² on.
Depending upon the type of coupling network employed, the Multivibfiltons ale classified into the following three categories.
1. Astable or free-running multivibrator.
2. Monostable or single-shot multivibrator.
3. Bistable of flip-flop multivibrator.
The first one is the non-driven type whereas the other two are the driven type (also called the triggered oscillators).
Multivibrators are used for various purposes such as the generation of nonsinusoidal waveforms (square, rectangular sawtooth, etc.) and pulses occurring periodically, frequency division, synchronized generation of pulses and extended waveforms, generation of time delays, storage of binary bit of information, etc.
1. Astable or Free Running Multivibrator.













It is really helpful.
ReplyDelete